Here are seven ways to check what version of MySQL you’re running.
Option 1: The @@version Variable
In MySQL, the @@version variable contains the server version number. It may also include a suffix with configuration or build information.
You can retrieve its contents with a simple SELECT statement.
Example:
SELECT @@version;Example result:
+-----------+ | @@version | +-----------+ | 8.0.29 | +-----------+
Option 2: The VERSION() Function
The VERSION() function returns the same information – the MySQL server version number, which may also include a suffix with configuration or build information.
This can be called using a SELECT statement. No arguments are required (or accepted).
Example:
SELECT VERSION();Result:
+-----------+ | VERSION() | +-----------+ | 8.0.29 | +-----------+
Option 3: The SHOW VARIABLES Statement
The SHOW VARIABLES statement shows the values of MySQL system variables.
You can use a WHERE clause to narrow the variables to just the version variable.
Example:
SHOW VARIABLES
WHERE variable_name = 'version';Result:
+---------------+--------+ | Variable_name | Value | +---------------+--------+ | version | 8.0.29 | +---------------+--------+
Alternatively, you can use a LIKE operator to return other variables that have version in their name.
Example:
SHOW VARIABLES
WHERE variable_name LIKE '%version%';Result:
+--------------------------+-----------------+ | Variable_name | Value | +--------------------------+-----------------+ | admin_tls_version | TLSv1.2,TLSv1.3 | | immediate_server_version | 999999 | | innodb_version | 8.0.29 | | original_server_version | 999999 | | protocol_version | 10 | | replica_type_conversions | | | slave_type_conversions | | | tls_version | TLSv1.2,TLSv1.3 | | version | 8.0.29 | | version_comment | Homebrew | | version_compile_machine | arm64 | | version_compile_os | macos12.2 | | version_compile_zlib | 1.2.11 | +--------------------------+-----------------+
Option 4: The STATUS Command
You can type STATUS any time you’re logged in to return information about the MySQL version and other details.
Example:
STATUS;Result:
mysql Ver 8.0.29 for macos12.2 on arm64 (Homebrew) Connection id: 8 Current database: Current user: root@localhost SSL: Not in use Current pager: stdout Using outfile: '' Using delimiter: ; Server version: 8.0.29 Homebrew Protocol version: 10 Connection: Localhost via UNIX socket Server characterset: utf8mb4 Db characterset: utf8mb4 Client characterset: utf8mb4 Conn. characterset: utf8mb4 UNIX socket: /tmp/mysql.sock Binary data as: Hexadecimal Uptime: 3 min 44 sec Threads: 2 Questions: 9 Slow queries: 0 Opens: 132 Flush tables: 3 Open tables: 53 Queries per second avg: 0.040
Option 5: Login to MySQL
When you first log in to MySQL, the version number is presented within the “Welcome” message.
For example, opening a new terminal window and running the following command connects to MySQL:
mysql -urootAnd the following “Welcome” (or similar) message is displayed:
Welcome to the MySQL monitor. Commands end with ; or \g. Your MySQL connection id is 8 Server version: 8.0.29 Homebrew Copyright (c) 2000, 2022, Oracle and/or its affiliates. Oracle is a registered trademark of Oracle Corporation and/or its affiliates. Other names may be trademarks of their respective owners. Type 'help;' or '\h' for help. Type '\c' to clear the current input statement.
Option 6: The --version Option
If you don’t have MySQL open, you can find out what version it is by using the --version (or -V) option of the mysql and mysqladmin programs.
For example, opening a new terminal window and running the following command:
mysql --versionReturns the following on my current system:
mysql Ver 8.0.29 for macos12.2 on arm64 (Homebrew)
And running the following command:
mysqladmin --versionReturns the following:
mysqladmin Ver 8.0.29 for macos12.2 on arm64 (Homebrew)
The --version part can alternatively be shortened to just --V.
Example:
mysql -VResult:
mysql Ver 8.0.29 for macos12.2 on arm64 (Homebrew)
Option 7: The GUI
If you’re connecting to MySQL via a graphical user interface (GUI), you might be able to see the version displayed somewhere in the GUI.
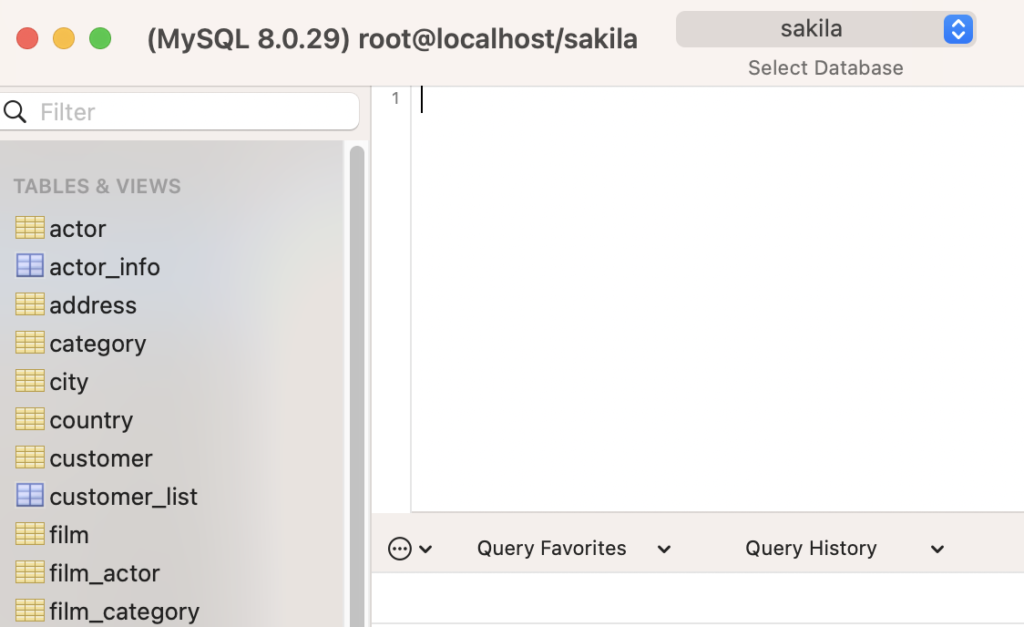
For example, when I connect to MySQL via Sequel Ace, the MySQL version is displayed in the top left of the GUI, along with connection information:
Option 8 (Bonus): The sys Schema Stored Functions
MySQL also has a bunch of sys schema stored functions, including a few that return information about the MySQL server version.
These are sys.version_major(), sys.version_minor(), and sys.version_patch().
Example:
SELECT
sys.version_major() AS major,
sys.version_minor() AS minor,
sys.version_patch() AS patch;Result:
+-------+-------+-------+ | major | minor | patch | +-------+-------+-------+ | 8 | 0 | 29 | +-------+-------+-------+